Find out more about the fascinating world of avian classification in this comprehensive article. Gain a better understanding of why birds are not considered mammals by exploring the defining characteristics of birds and mammals.
We explore the unique characteristics of birds as well as the diverse traits of mammals, including their classifications, reproductive strategies, coverings (feathers vs. fur), and metabolic adaptations. Identify the differences between these two groups of animals in terms of their evolutionary paths. Discover how birds and mammals differ within the animal kingdom on this journey of discovery.
Understanding Bird Classification
Definition of Birds
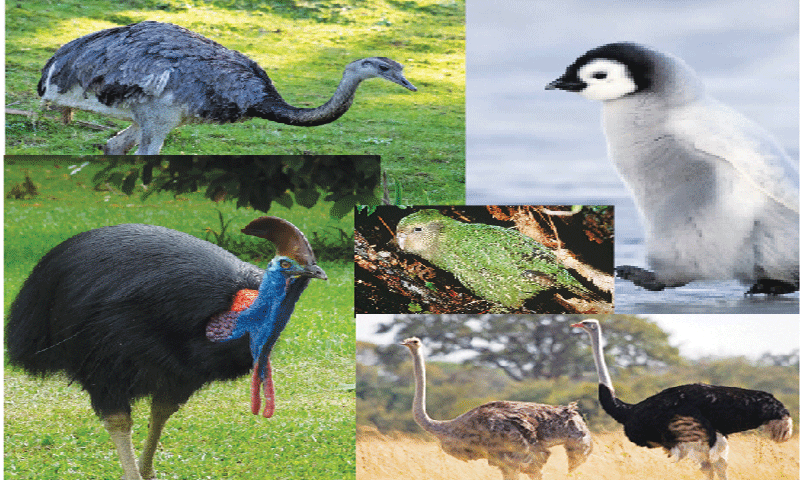
A bird is a warm-blooded vertebrate belonging to the family Aves. Among other things, they are known for their ability to fly, although not all birds possess this ability. Among birds, more than 10,000 species are exhibiting a wide range of sizes, colors, beak shapes, and habitat preferences. From forests and deserts to oceans and cities, they can be found in a wide variety of ecosystems throughout the world.
Key Characteristics of Birds
Several key characteristics define the classification of birds. Among their most prominent characteristics are their feathers, which are unique to birds and serve several functions, including flight, insulation, and courtship displays. Moreover, birds possess beaks or bills, two legs adapted for walking and perching, and lay hard-shelled eggs.
Classification of Birds
Find out more about the fascinating world of avian classification in this comprehensive article. Gain a better understanding of why birds are not considered mammals by exploring the defining characteristics of birds and mammals.
Understanding Bird Classification
Definition of Birds
A bird is a warm-blooded vertebrate belonging to the family Aves. Among other things, they are known for their ability to fly, although not all birds possess this ability. Among birds, more than 10,000 species are exhibiting a wide range of sizes, colors, beak shapes, and habitat preferences. From forests and deserts to oceans and cities, they can be found in a wide variety of ecosystems throughout the world.
Key Characteristics of Birds
Several key characteristics define the classification of birds. Among their most prominent characteristics are their feathers, which are unique to birds and serve several functions, including flight, insulation, and courtship displays. Moreover, birds possess beaks or bills, two legs adapted for walking and perching, and lay hard-shelled eggs.
Classification of Birds
Based on their anatomical, physiological, and genetic characteristics, birds are further categorized into orders, families, genera, and species. Passeriformes (songbirds), Falconiformes (raptors), and Strigiformes (owls) are some of the most well-known bird orders. The hierarchical classification system allows scientists to organize and study the vast number of bird species that can be found throughout the world.
Differentiating Birds from Mammals
Definition of Mammals
A mammal, on the other hand, belongs to the class Mammalia. It is characteristic of them that they possess mammary glands that produce milk to nourish their young. The body of mammals is also covered in fur or hair, has a four-chambered heart, and has a diaphragm specialized for breathing.
A wide variety of mammal species are found on earth, from little shrews to majestic elephants, as well as agile cheetahs to intelligent dolphins. Mammals have approximately 5,500 species and range from tiny shrews to majestic elephants.
Key Characteristics of Mammals
There are several distinctive characteristics that set mammals apart from other animals. Mammary glands are one of the most distinctive characteristics of mammals. These glands produce milk to feed their young.
The dentition of mammals is also specialized, consisting of different types of teeth that serve a variety of functions, including grinding, tearing, and chewing. Additionally, their well-developed neocortex, which is associated with complex cognitive capabilities, is a defining characteristic of their species.
Contrasting Birds and Mammals
There are some similarities between birds and mammals, but there are also significant differences between them. Feathers are found in birds, whereas fur or hair is found in mammals.
The majority of mammals give birth to live young, unlike birds that lay hard-shelled eggs. Mammals have an internal skeleton that is made up of bones, whereas birds have lightweight skeletons adapted for flight. As a result of these differences, it is clear how these two groups of animals have evolved in very different ways.
Why Birds Are Not Mammals?
Reproduction and Offspring
There is a fundamental difference between the reproductive strategies of birds and mammals. The eggs of birds are laid and then incubated until they hatch. As opposed to mammals, which have internal fertilization and produce live young, mammals have internal fertilization. It is important to note that birds have feathers and are capable of laying eggs, which distinguish them from mammals.
Feathers vs. Fur
A bird’s feathers play a critical role in its survival. They are unique to birds and are essential to their survival. Insulation is provided by them, the flight is enabled by them, and courtship displays are facilitated by them. Mammals, on the other hand, possess fur or hair that serves as insulating, camouflaging, and sensory protection. In birds and mammals, feathers and fur are distinct adaptations that have evolved separately, further emphasizing their differences.
Warm-Blooded vs. Cold-Blooded
A warm-blooded animal is either a bird or a mammal, which means they are capable of regulating their internal body temperature. The metabolism of birds is higher than that of mammals, which allows them to generate more heat. Birds can fly as a result of their increased metabolic rate, which requires them to expend a significant amount of energy. There is also a higher energy demand for mammals than for other animal groups, however, their physiological adaptations to keep themselves warm are different from those of other animal groups.
Must Read: Types & Unique Characteristics of Fish with Teeth
Conclusion
The animal kingdom is divided into two categories: birds and mammals. Aves are a group of animals that include birds because of their feathers, beaks, and ability to lay hard-shelled eggs. Class Mammalia includes mammals with fur or hair, mammary glands, and the ability to nurse their young with milk.
The characteristics of birds and mammals are similar in some respects, for instance, both are warm-blooded, but they differ significantly in terms of reproduction, cover (feathers versus fur), and metabolic adaptations. The distinctions between these types of animals emphasize the diversity of adaptations that have evolved.