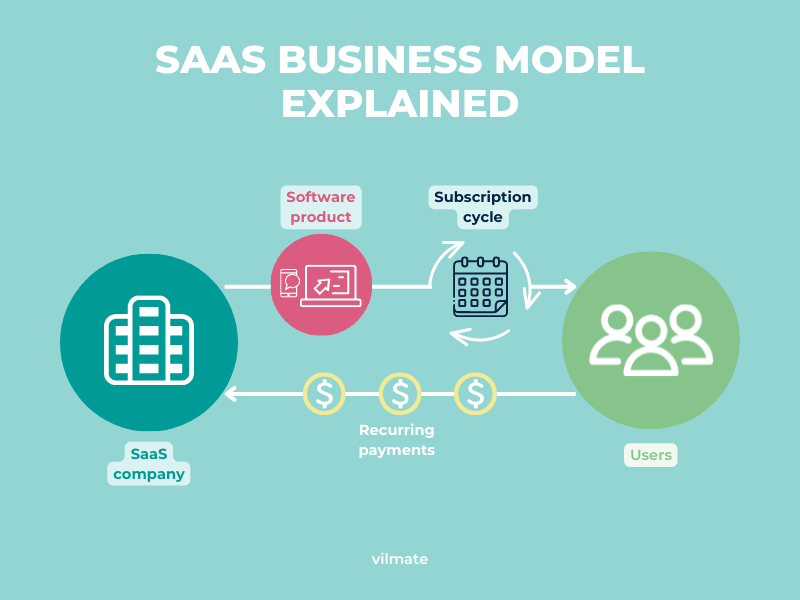
The primary mode of operation for any subscription-based software-as-a-service provider is the SaaS recurring revenue model. Analysis of recurring revenue enables a SaaS or any other organization to identify crucial trends in the lifetime of the business. This research’s findings heavily influence recurring revenue management. Analytical data enables management to fine-tune the operations of the SaaS business in order to optimize the value of existing subscribers, attract new consumers, and respond to current difficulties.
What is Recurring Revenue Business Model for SaaS?
Recurring payments are the main source of income for many SaaS businesses. In other words, clients pay for goods and services on a consistent basis in accordance with predetermined subscription agreements. In essence, a subscription plan is a subscriber’s promise to make regular, set payments. Utility bills and charges for using the pool or using the Internet are a few examples of recurrent payments. A prominent candidate for the deployment of a SaaS recurring revenue mode is a company that offers services to a network of fitness facilities.
So, what is recurring revenue?
The value of each subscription, normalized by the duration of the time period, is what is known as recurring revenue. It is often a month or a year. Monthly recurring revenue is frequently used by SaaS and other subscription-based businesses to determine customer value, anticipated revenues, and selling pricing.
Businesses with recurring revenue should consider two critical factors. An example of a technological aspect would be payment processing-related elements. The business aspect contains elements that are connected to the cycle of regular billing.
SaaS Recurring Revenue Model: Billing-related Factors
Four main characteristics support contemporary recurring revenue models. Three are favorable, and one is unfavorable.
- The value of subscription plan upgrades is the expansion of monthly recurring revenue.
- Reactivation of monthly recurring revenue is the value of accounts for reactivated subscribers.
- New monthly recurring revenue is the benefit that new clients provide.
- Churn monthly recurring revenue is the value of canceled and reduced subscriptions.
The first three factors influence revenue growth, but the fourth factor is just as significant.
Businesses with recurring revenue have to monitor all four variables and track changes in each. They will be able to identify the advantages and disadvantages of the selected recurring revenue models and tactics as a result. Additionally, they will recognize the causes of client churn and take action to avoid it.
SaaS Recurring Revenue Model: Processing-related Factors
This category of variables is influenced by the causes and numbers (both absolute and relative) of transaction reductions.
Recurring declines in recurring revenue models frequently have the same root cause. These are some typical explanations.
- Insufficient resources Transactions in these circumstances ought to be retried utilizing decline recycling logic.
- The card number or expiration date is not valid. When the card kept on file expires, this frequently occurs. Recurring revenue SaaS should have account updater logic set up for such circumstances.
- The transaction’s formatting needs to be corrected. For example, a “recurring” indicator is frequently absent from transaction description formats, which results in many transactions being rejected.
If research reveals that there are any common causes of transaction decreases, the business may be able to address the problems that underlie these declines.
Analysis of Declined Transactions
What insights can we get from the analysis on the nature and common causes of declines?
- Declines that are most typical.
- Kinds of refused transactions that need to be retried.
- Typical situations where the business must check or modify cardholder information and inform consumers.
- Common circumstances where the business must use account updater logic.
The business will be able to lower the transaction decline rate and boost subscription income.
Processing costs
When selecting a payment gateway or processor, the transaction cost is one of the most crucial considerations. It is applicable to SaaS’s recurring revenue model as well. Small business owners are frequently forced to accept the processing terms (and set costs) that major suppliers provide. At the same time, bigger SaaS businesses that use the cost-plus model should examine the quantities and elements of interchange fees they incur. Processing some recurring payment types, for example, is too costly. In such instances, it may be fair to urge clients to use alternative payment methods.
Conclusion
A SaaS organization must examine both the commercial and technological facets of the procedure in order to assure effective recurring revenue management for both itself and its clients. Any successful SaaS recurring revenue model must start with an understanding of the most frequent causes of transaction decreases, account freezes, and customer churn. Important client categories are represented by recurring revenue enterprises and SaaS providers.
UniPay Gateway, our flagship product, also has a specific solution (UniBill) for the efficient processing of recurring payments.
So, please contact our specialists at UniPay Gateway to learn more about how the SaaS recurring revenue model might work for your unique business model.