Bitcoin, the pioneer of cryptocurrencies, has sparked a global financial revolution since its inception in 2009. Understanding the underlying technology that powers Bitcoin—blockchain—is essential in comprehending its significance. In this article, we will delve deep into the intricacies of Bitcoin and explore the fundamental building blocks of this groundbreaking digital currency. If you’re new to Bitcoin and thinking about investing, Immediate Vortex is a reliable tool to start your journey into cryptocurrency trading.
What is Bitcoin?
Historical Context and the Mystery of Satoshi Nakamoto
Bitcoin emerged in the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis, introduced by an enigmatic figure known as Satoshi Nakamoto. Nakamoto’s true identity remains unknown, but the whitepaper, “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System,” presented the world with the concept of a decentralized digital currency.
Defining Bitcoin as a Decentralized Digital Currency
At its core, Bitcoin is a digital currency that operates outside traditional financial systems. It enables peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks. Bitcoin’s decentralized nature ensures that no single entity has control over it, making it resistant to censorship.
Key Features and Benefits of Bitcoin
Bitcoin offers several key features and benefits, including security through cryptographic techniques, transparency through a public ledger, and borderless transactions. Its finite supply of 21 million coins ensures scarcity and potential value appreciation.
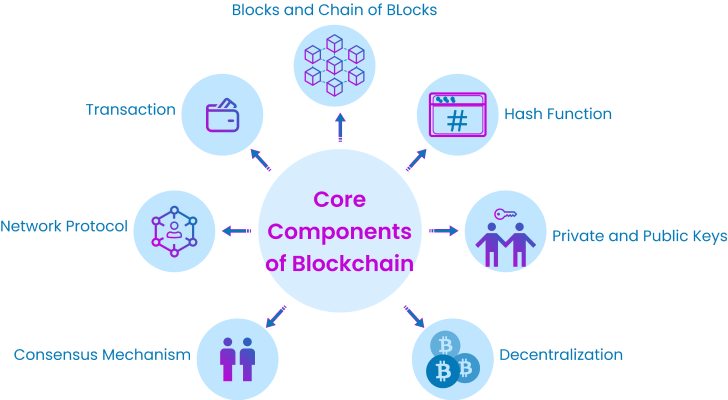
Blockchain Technology
Introduction to Blockchain as the Foundation of Bitcoin
Blockchain serves as the technological backbone of Bitcoin. It is a distributed ledger that records all transactions made on the network. Transactions are grouped into blocks, which are added to the chain in chronological order.
How Blockchain Works: Blocks, Transactions, and Consensus
Blockchain consists of a series of blocks, each containing multiple transactions. These blocks are linked together through cryptographic hashes, creating an immutable chain. The consensus mechanism, typically Proof of Work (PoW) in Bitcoin, ensures agreement among network participants on the validity of transactions and the order of blocks.
The Role of Miners and Nodes in the Bitcoin Network
Miners play a crucial role in the Bitcoin network. They compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles in a process known as mining. Once a miner successfully solves a puzzle, they add a new block to the blockchain and receive a reward in Bitcoin. Nodes, on the other hand, validate and propagate transactions, ensuring the network’s integrity.
Decentralization and Security
Exploring the Concept of Decentralization in Bitcoin
Bitcoin’s decentralization means that no central authority governs it. Instead, it relies on a network of nodes and miners distributed worldwide. This decentralization fosters trust and resilience, as the network isn’t susceptible to single points of failure.
Security Measures and Cryptographic Techniques
Bitcoin employs robust cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and wallets. Public and private keys are used for ownership verification, while cryptographic hashing ensures the integrity of data within each block. This cryptographic security makes it extremely difficult for malicious actors to alter the blockchain.
Immutability and Resistance to Censorship
Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes virtually immutable. Altering a single transaction would require an infeasible amount of computational power, reinforcing the integrity of the Bitcoin ledger. This immutability also makes Bitcoin resistant to censorship, as no central authority can control or manipulate it.
Transaction Process
Step-by-Step Breakdown of a Bitcoin Transaction
Bitcoin transaction involves several steps:
- Initiating the transaction: A sender creates a transaction request.
- Verification: The transaction is validated by nodes on the network.
- Inclusion in a block: Miners include the transaction in a block they are mining.
- Confirmation: Once the block is added to the blockchain, the transaction is considered confirmed.
Address Generation and Ownership Verification
Users generate unique addresses for receiving Bitcoin. These addresses are derived from their public keys. Ownership of Bitcoin is verified using digital signatures associated with private keys, ensuring the security of funds.
Confirmations and the Double-Spending Problem
Confirmations represent the number of blocks added to the blockchain after a transaction. As more blocks are added, the likelihood of a transaction being reversed decreases, addressing the double-spending problem—the risk of spending the same Bitcoin twice.
Mining and Rewards
Understanding the Mining Process
Mining involves solving complex mathematical puzzles using computational power. Miners compete to find the solution to a puzzle, and the first one to succeed gets the privilege of adding a new block to the blockchain. This process is resource-intensive and serves as the backbone of Bitcoin’s security.
Role of Miners in Securing the Network
Miners play a vital role in securing the network by confirming transactions and adding them to the blockchain. In return, they receive Bitcoin rewards, both from transaction fees and newly created Bitcoins. The mining process ensures the integrity and decentralization of Bitcoin.
Bitcoin Rewards and the Halving Mechanism
Bitcoin’s issuance rate is programmed to decrease over time through a process called halving. Initially, miners received 50 Bitcoins per block, but this reward is halved approximately every four years. The latest halving event in May 2020 reduced the reward to 6.25 Bitcoins per block, contributing to Bitcoin’s scarcity.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Scalability Issues and Proposed Solutions
Bitcoin faces scalability challenges, as the network’s capacity to process transactions is limited. Solutions like the Lightning Network aim to enhance scalability by enabling off-chain transactions, reducing congestion on the main blockchain.
Environmental Concerns and Green Alternatives
The energy-intensive nature of Bitcoin mining has raised environmental concerns. Some proponents are exploring greener alternatives to PoW, such as Proof of Stake (PoS), to reduce the carbon footprint associated with cryptocurrency mining.
The Evolving Landscape of Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain Technology
Bitcoin paved the way for thousands of other cryptocurrencies and blockchain projects. The crypto space continues to evolve, with new innovations and applications emerging in areas like decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and more.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Bitcoin’s remarkable success as a decentralized digital currency is intricately linked to the groundbreaking blockchain technology that forms its foundation. Gaining a profound understanding of Bitcoin’s core elements, ranging from its decentralized architecture and robust cryptographic security to the intricate mining process and scalability challenges, is imperative for individuals seeking to navigate the dynamic realm of cryptocurrency. As the cryptocurrency landscape continually evolves, it is essential to remain well-informed about these fundamental concepts. For staying updated on the latest developments in the crypto domain, exploring reputable sources like “Bitcoin Era” can offer invaluable insights and knowledge to enthusiasts and investors alike.